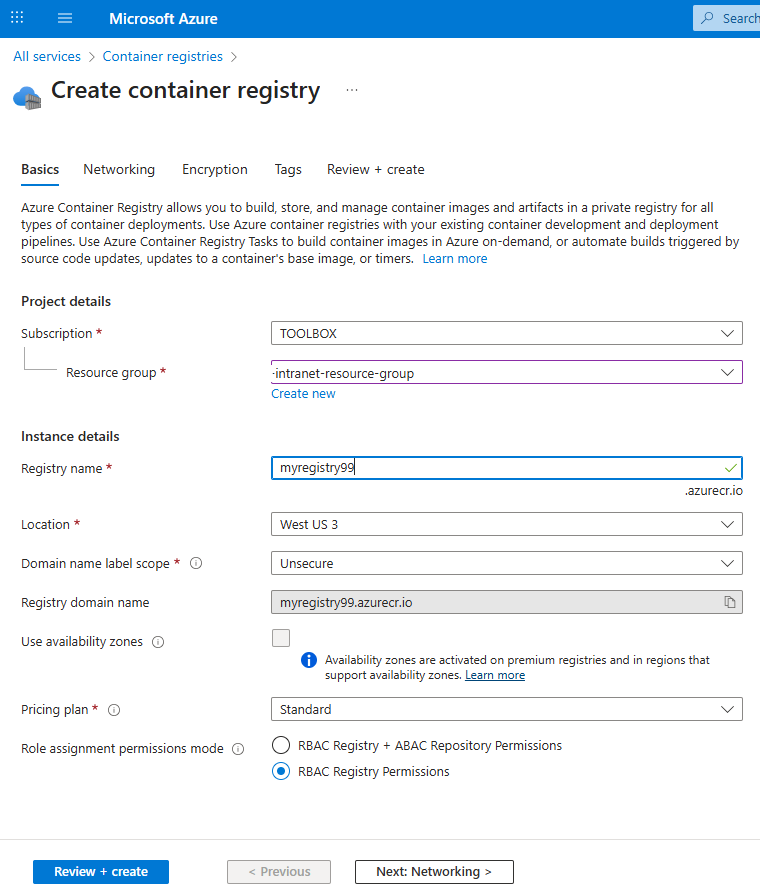
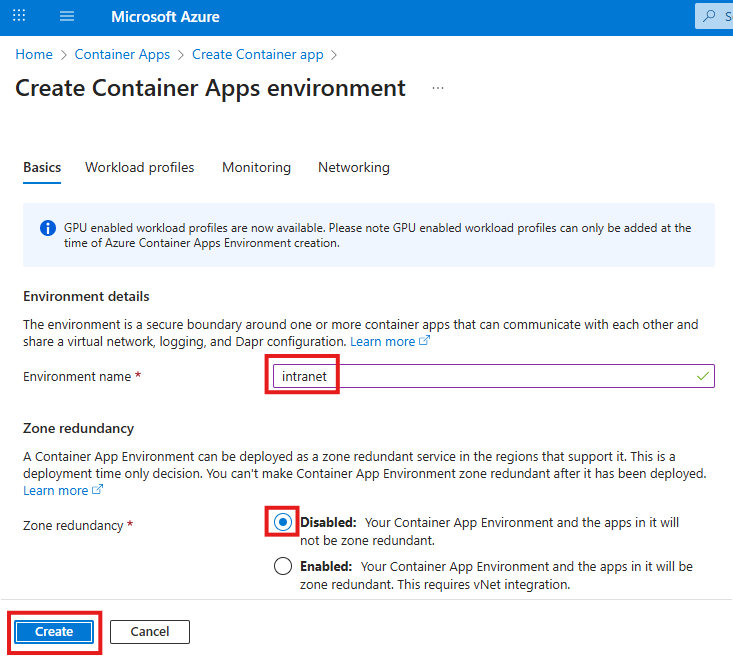
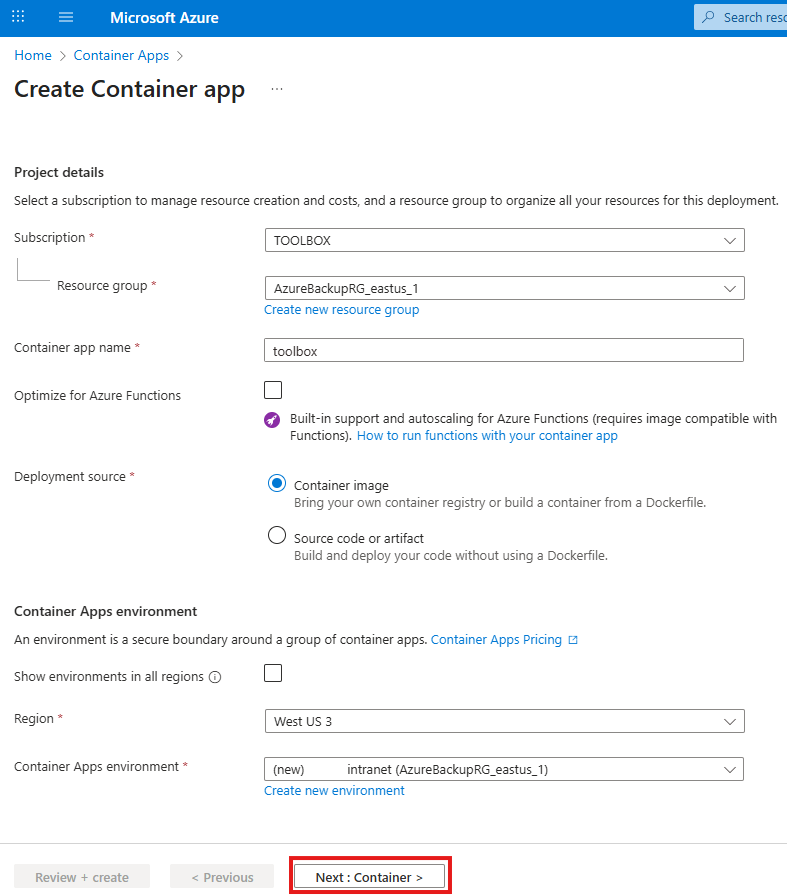
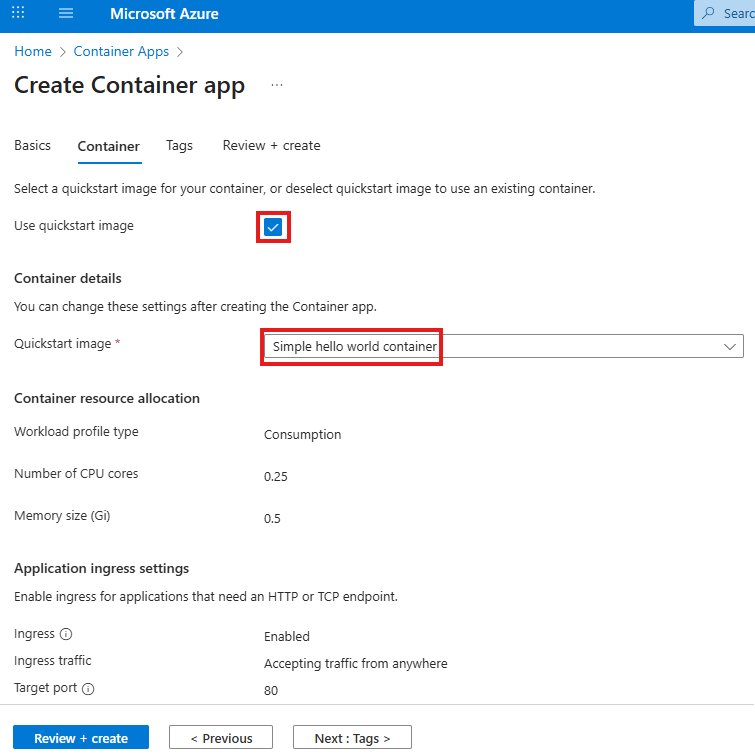
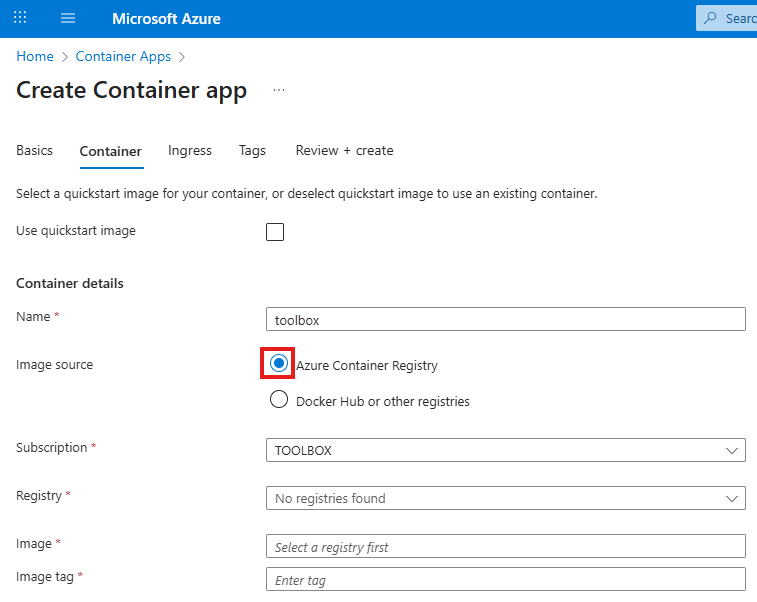
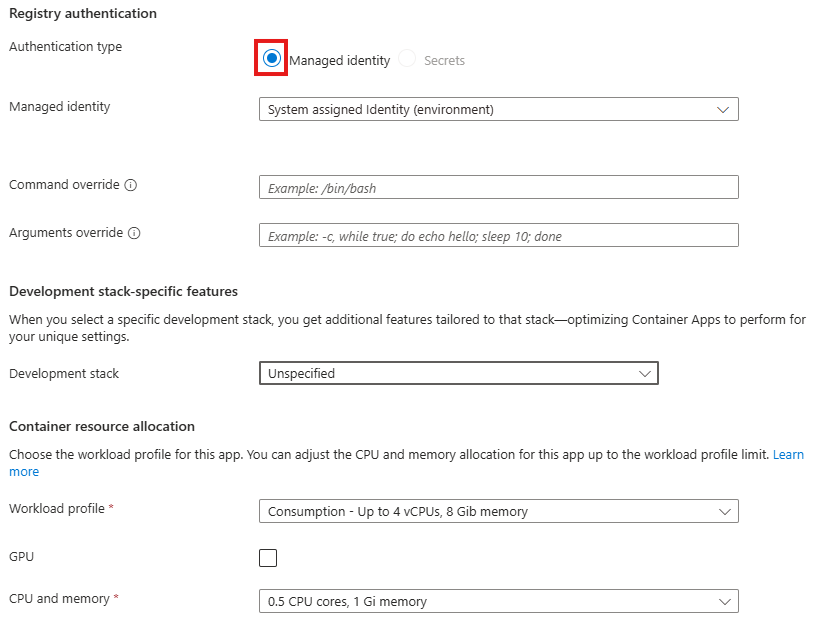
Tailwind is a rapid web development tool to style user interfaces using English like expressions. It has advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
Instead of complex CSS, use English like style class names to control all aspects of the web interface
Disadvantages
When we use CSS, we create classes to style similar elements, like submitButton, searchField. Tailwind classes define a specific visual property, like background, border, text color. There is no room to create styles for similar objects. Using Tailwind it can be tedious to keep the visuals consistent in a large web application. If we want to update the style of all buttons on multiple pages, we have to visit all of them to change the class names.
In this tutorial we will develop a system that merges the advantages of the CSS thematic classes and the friendliness of Tailwind.
We will create a class collection, a middle layer between the Tailwind classes and the elements to specify the look of all controls with the same purpose. You still can override the values at the individual control level with the ! (important) postfix.
Class collection
Create the styles/classes.ts file in the same directory where the style sheets are located for consistency. In this example we will create separate themes for the panel header, and the panel body. All contains light and dark mode Tailwind classes for background, border, button text, hover styling.
// Define color themes for different panel types
// Each theme includes classes for borders, backgrounds, text, inputs, buttons, and drag states
export const ColorThemes = {
panelHeader: {
bg: "bg-slate-200 dark:bg-slate-700",
text: "text-black dark:text-white",
input: "bg-white dark:bg-slate-600 text-black dark:text-white placeholder:text-slate-500 dark:placeholder:text-slate-400",
button: "bg-black/50 dark:bg-white/20 text-white/80 dark:text-white hover:bg-black/40 dark:hover:bg-white/50",
},
panelBody: {
border: "border-blue-200 dark:border-slate-600",
bg: "bg-slate-100 dark:bg-slate-700",
text: "text-blue-200 dark:text-blue-800",
hover: "hover:bg-blue-100 dark:hover:bg-slate-700",
button: "bg-blue-600 dark:bg-blue-800 hover:bg-blue-500 dark:hover:bg-blue-700",
},
};
Usage
In the .tsx file import the class collection and create constant references.
// Import color themes to standardize appearance for light and dark modes
import { ColorThemes } from "~/styles/classes";
Style the controls. Enclose the entire className definition in curly braces, and use backtick to allow variable usage in the string. You can add additional Tailwind classes to the element to set specific visual features.
<div className={`${ColorThemes.panelBody.bg} ${ColorThemes.panelBody.border} rounded-xl`} >
To override the background color for this element, use the ! (important) postfix
<div className={`${ColorThemes.panelBody.bg} bg-black! rounded-xl`} >